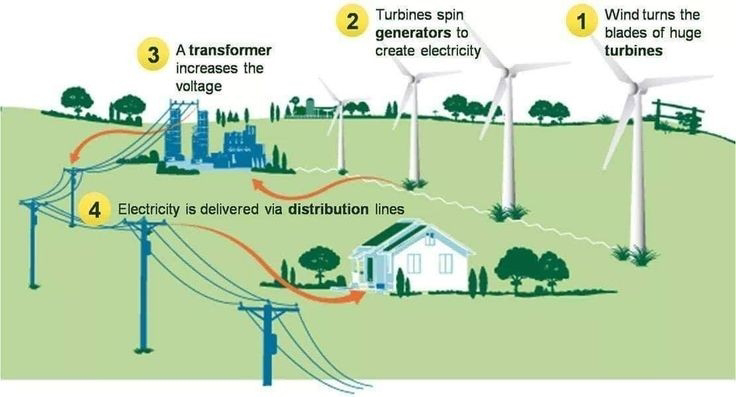
A coal power plant is a type of power station that generates electricity by burning coal. Coal is a fossil fuel that is mined from the ground, and when it is burned, it releases energy in the form of heat. This heat is used to produce steam, which drives a turbine that generates electricity.
Coal power plants are one of the most common types of power plants in the world, and they have been used for many decades to generate electricity. However, they are also one of the largest sources of greenhouse gas emissions, as burning coal releases carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and other pollutants into the atmosphere. These emissions have been linked to climate change and negative health impacts.
In recent years, there has been a shift towards cleaner forms of energy, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, as well as a greater emphasis on energy efficiency and conservation. However, coal power plants remain an important source of energy in many countries, particularly in developing countries where they may be the most cost-effective option for meeting growing energy demands.
A coal power plant typically consists of several main components, including:
Coal handling and storage system: This component is responsible for receiving, storing, and preparing the coal for combustion. The coal may be transported to the plant by train, truck, or conveyor belt, and is typically stored in large silos or bunkers.
Boiler: The boiler is the heart of the power plant, where the coal is burned to produce steam. The steam is then used to drive a turbine that generates electricity. The boiler consists of a combustion chamber, where the coal is burned, and a series of tubes or pipes through which water flows to be heated by the hot gases produced by the combustion process.
Turbine: The turbine is connected to the generator and is responsible for converting the energy in the steam into mechanical energy. As the steam passes through the turbine blades, it causes the blades to rotate, which in turn rotates the generator to produce electricity.
Generator: The generator is responsible for converting the mechanical energy produced by the turbine into electrical energy that can be used by homes, businesses, and other consumers.
Cooling system: The cooling system is used to cool the steam after it has passed through the turbine so that it can be condensed back into water and returned to the boiler to be heated again. This is typically done using water from a nearby river or lake, which is circulated through a series of pipes to absorb the heat from the steam.
Pollution control equipment: Pollution control equipment is used to reduce the emissions of pollutants from the power plant. This may include scrubbers, which remove sulfur dioxide and other pollutants from the flue gas, or electrostatic precipitators, which remove particulate matter from the flue gas.
Transmission lines: Once the electricity is generated, it is transmitted to the electrical grid through a network of transmission lines and substations. The electricity can then be distributed to homes, businesses, and other consumers.
There may also be other auxiliary systems within a coal power plant, such as water treatment systems, ash handling systems, and control systems to monitor and regulate the operation of the plant.
One of the main advantages of coal power plants is that they are relatively cheap to build and operate compared to other forms of power generation. Coal is a relatively abundant and inexpensive fuel, and the technology for burning coal to produce electricity is well-established and widely available.
However, coal power plants are also a major source of air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Burning coal releases large amounts of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming, as well as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants that can harm human health and the environment. These emissions can be reduced through the use of pollution control technologies, such as scrubbers and filters, but these technologies can add to the cost of operating a coal power plant.
Another challenge associated with coal power plants is the environmental impact of coal mining. Coal mining can have significant impacts on land use, water quality, and wildlife habitat, and can also cause health problems for miners and nearby communities due to exposure to coal dust and other pollutants.
Despite these challenges, coal power plants continue to play an important role in the global energy mix. However, there is a growing recognition of the need to transition away from fossil fuels towards cleaner forms of energy in order to address climate change and reduce air pollution. This has led to increased investment in renewable energy sources and the development of new technologies, such as carbon capture and storage, that could help to reduce the environmental impact of coal power plants.