Initially, we discussed in a previous post that a fault is divided into three parts: Pre-fault, Fault, and Post-fault.
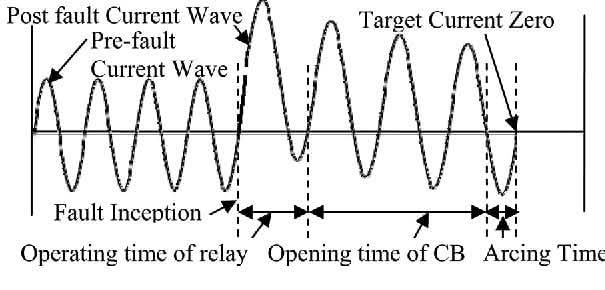
The Pre-fault phase is the beginning of the fault. Let's assume the protection relay operating time is 1.5 seconds.
If a fault occurs but does not last for 1.5 seconds, it is called a Transient Fault, such as an Inrush Current fault in transformers.
If the fault persists for 1.5 seconds, the protection relay sends a Trip signal to the circuit breaker (C.B).
The Tripping Time of the circuit breaker is the time measured during the circuit breaker tests, along with the Closing Time.
There is another time called the C.B Arcing Time, which is the time required to extinguish the arc generated during the tripping process, typically ranging between 5 and 10 milliseconds.
The sum of these three times is called the Total Fault Clearing Time, which is the total time required to isolate the fault.







No comments:
Post a Comment