Here’s a brief explanation of the key components and the overall concept:
Key Components:
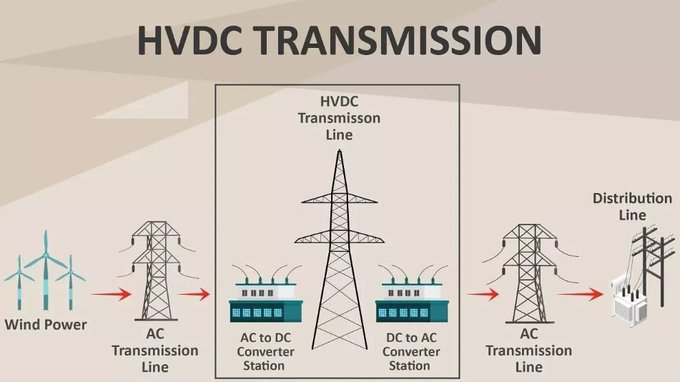
1. Wind Power Generation:
- The process begins with wind turbines generating electricity. This is typically in the form of Alternating Current (AC).
2. AC Transmission Line:
- The generated AC power is transmitted through high-voltage AC transmission lines. This is the traditional method of electricity transmission.
3. AC to DC Converter Station:
- At a strategic point along the transmission line, an AC to DC converter station transforms the AC power into High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC). This conversion is essential for long-distance transmission as DC power experiences lower losses compared to AC.
4. HVDC Transmission Line:
- The HVDC transmission line carries the high-voltage direct current over long distances. This method is particularly beneficial for reducing energy losses and improving the stability of the power grid.
5. DC to AC Converter Station:
- Upon reaching the destination, another converter station changes the HVDC back into AC, making it suitable for distribution through local AC transmission lines.
6. Distribution Line:
- Finally, the converted AC power is sent through distribution lines to homes, businesses, and other end users.
Concept Overview:
HVDC transmission is an advanced technology that allows for the efficient transfer of electrical energy across long distances. It minimizes energy losses that typically occur in traditional AC transmission systems, especially when dealing with high power demands. HVDC is particularly useful for integrating renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, into the grid, as it facilitates the connection of remote energy generation facilities to urban centers. Overall, HVDC transmission enhances the reliability and efficiency of power systems while supporting the transition to cleaner energy sources.





No comments:
Post a Comment