Electrical power distribution is the final stage in the delivery of electricity. Electricity is carried from the transmission system to individual consumers.
The electrical distribution system consists of three major components:
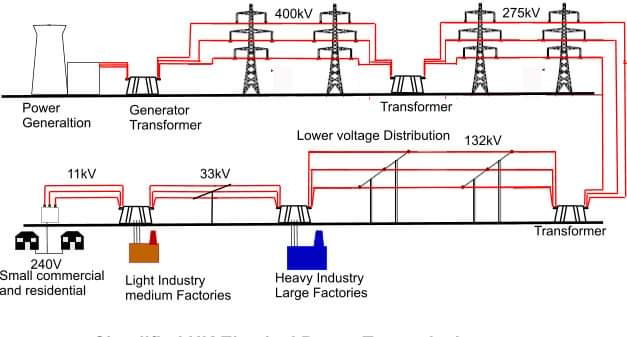
1. Generation: Electricity is generated at power plants, which can be fueled by coal, natural gas, nuclear power, hydroelectric power, or other sources.
2. Transmission: Electricity is transmitted from power plants to distribution substations over high-voltage transmission lines.
3. Distribution: Electricity is distributed from distribution substations to individual consumers over low-voltage distribution lines.
The distribution system is a complex network of wires, transformers, and other equipment that is essential to the delivery of electricity to homes and businesses. The system must be able to handle the large amount of electricity that is used by consumers, and it must be able to do so safely and reliably.
The distribution system is divided into two main parts:
1. Primary distribution: Primary distribution lines carry electricity from distribution substations to large consumers, such as factories and businesses.
2. Secondary distribution: Secondary distribution lines carry electricity from
distribution substations to individual homes and businesses.
Primary distribution lines are typically high-voltage lines that are located above ground. Secondary distribution lines are typically low-voltage lines that are located underground or below ground.
The distribution system is a vital part of the electrical grid. It is responsible for delivering electricity to homes and businesses, and it plays a critical role in the economy.
Here are some of the key components of an electrical power distribution system:
1. Distribution substations: Distribution substations are located throughout the distribution system. They connect the transmission system to the distribution system, and they also provide voltage regulation and protection for the distribution system.
2. Transformers: Transformers are used to step up or down the voltage of electricity. This is necessary because the voltage of electricity that is transmitted over long distances is much higher than the voltage that is used by homes and businesses.
3. Distribution lines: Distribution lines are the wires that carry electricity from distribution substations to homes and businesses. Distribution lines can be either overhead or underground.
3. Switchgear: Switchgear is used to control the flow of electricity in the distribution system. This is necessary to protect the system from overloads and to ensure that electricity is delivered to the right places.
4. Metering: Metering is used to measure the amount of electricity that is used by homes and businesses. This information is used to bill customers for their electricity usage.
The electrical power distribution system is a complex and essential part of the electrical grid. It is responsible for delivering electricity to homes and businesses, and it plays a critical role in the economy.





No comments:
Post a Comment