Welcome to SparkED, your ultimate destination for all things engineering, science, and innovation! Our blog is a vibrant platform dedicated to showcasing the latest advancements, groundbreaking research, and fascinating discoveries in the world of electrical engineering and beyond. At SparkED, we believe in the power of knowledge and its ability to ignite extraordinary ideas. Our team of passionate writers and researchers is committed to bringing you captivating articles.
Sunday, 29 October 2023
What is a biogas?
 At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
Saturday, 28 October 2023
There are 486,713 routes to Rome
 At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
Ranveer Singh revealed about RaamLeela first actress
 At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
Saturday, 21 October 2023
What is a power factor?
 At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
Wednesday, 18 October 2023
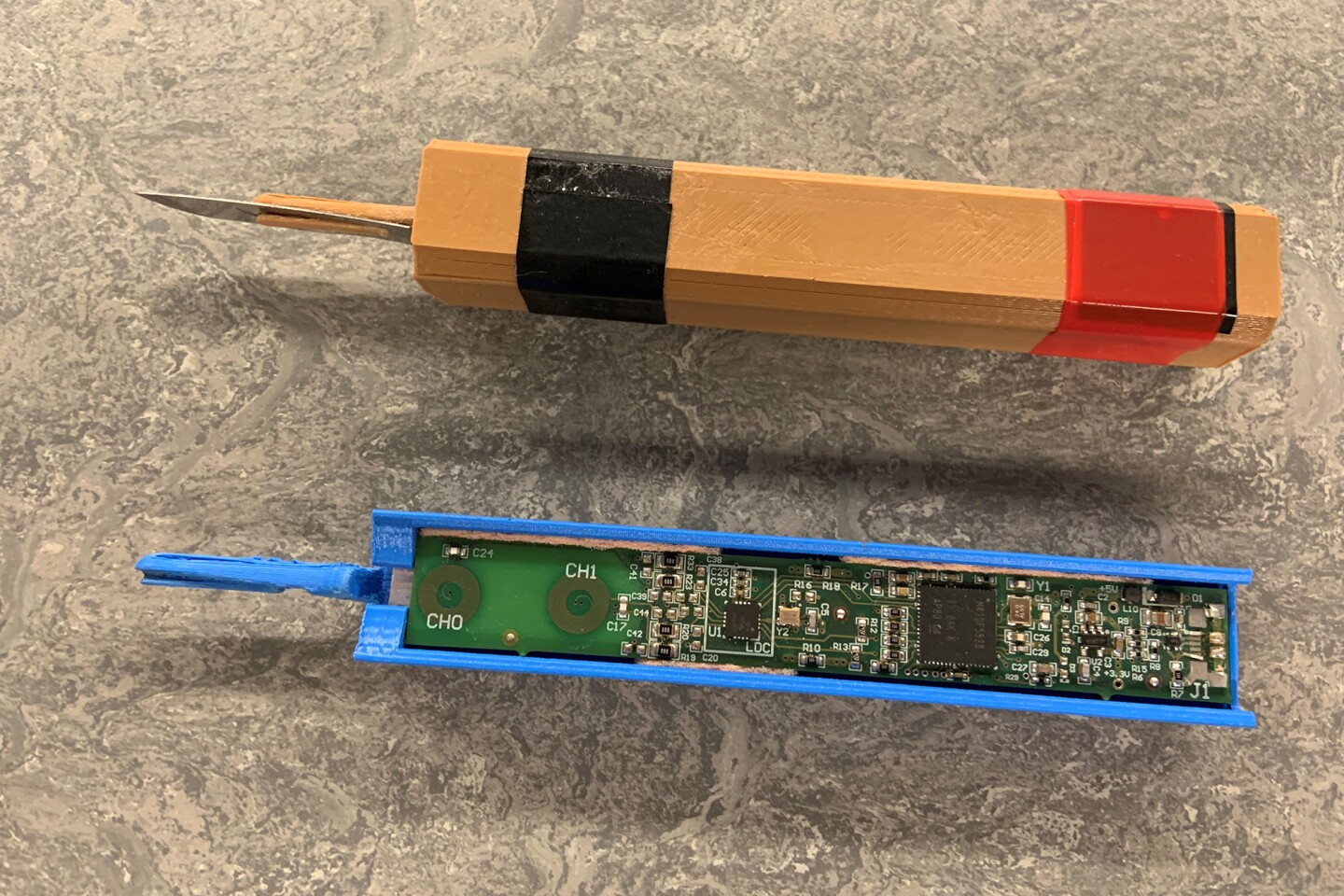
Force-sensing ‘smart scalpel’ helps hone doctors’ surgical skills
While the level of force applied to the scalpel by its human operator is – obviously – important during surgery, there have been few tools capable of measuring it in real-life settings. Now, researchers at the University of Edinburgh in the UK have developed a ‘smart scalpel’ with built-in sensors to measure force.
“We are excited to develop this new system, which uses a combination of real-life sensing technology and machine learning methods to quantitatively assess surgical skill,” said Ram Ramamoorthy, the study’s corresponding author. “This system will enable the development of new systems for skill assessment and training and could one day lead to the creation of automated surgical devices that can assist surgical teams.”
The low-cost, easy-to-replicate device consists of a scalpel connected to a sensor-loaded circuit board fitted inside its handle. The researchers designed a machine-learning model to analyze the force applied by the users. Twelve medical students and two professional surgeons tested their innovative scalpel by performing a series of 12 elliptical incisions on a multilayered skin replica made of gelatin and silicone.
Each procedure, which involved making two curved cuts to the skin, such as those used to remove moles and melanomas, was video-recorded and assessed by four expert surgeons – two neurosurgeons and two plastic surgeons – who rated the participants’ proficiency. The researchers then analyzed the relationships between the subjective expert evaluations and the objective force-based metrics data.
Results broadly matched the surgical experts’ assessment of each medical student’s ability, suggesting that this technology could simplify the process of assessing surgical skills. Some discrepancies arose, which, the researchers say, are partly because neurosurgeons and plastic surgeons use different instrument and tissue handling techniques.
The researchers say their findings open up possibilities for future studies, including using more participants for a more comprehensive analysis. Mapping objective measurements and patient outcomes would also be instructive. They say their method shows promise as a way of analyzing highly procedural tasks such as suturing.
The study was published in the journal Communications Engineering.
 At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
Amazon river hits century-low water levels; record drought disrupts lives in Brazilian rainforest
 At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
Tuesday, 17 October 2023
What is and Auto - Recloser?
 At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
At SparkED, we strongly believe in supporting and promoting the work of young researchers and scientists. We are interested in featuring and showcasing the groundbreaking studies, experiments, and ideas of emerging talents who are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation.
-
Transformers are rated in kVA (kilovolt-amperes) because they supply both active (real) and reactive power, and their losses dep...
-
Why Grounding Wires Are Not Insulated? Grounding wires, also known as earthing wires, are left uninsulated for safety reasons. Here are some...
-
In a three-phase system, the voltage between two phases is not simply the sum of the individual phase voltages (220V + 220V = 44...