Capacitors:
Capacitors are electronic components used for storing electrical energy. They are made up of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material (dielectric).
Characteristics of Capacitors
1. Storage Capacity:
- Capacitors have a measure of capacitance, typically expressed in farads (F). One farad can store one coulomb of charge at one volt of electrical potential.
2. Dielectric Materials:
- The insulating materials between the plates can vary and include paper, ceramic, plastic, and liquids, depending on the capacitor's specifications and applications.
3. Voltage Rating:
- Each capacitor has a specified voltage it can handle. Exceeding this voltage may damage the capacitor.
Types of Capacitors
1. Ceramic Capacitors:
- Suitable for high-frequency applications, typically with lower capacitance values.
2. Electrolytic Capacitors:
- Used for high capacitance applications, commonly found in DC circuits.
3. Film Capacitors:
- Ideal for stable and precise capacitance values.
4. Variable Capacitors:
- Used for changing capacitance values, such as in radio frequency applications.
Applications of Capacitors
- In Electronic Circuits: For energy storage, voltage regulation, and frequency tuning.
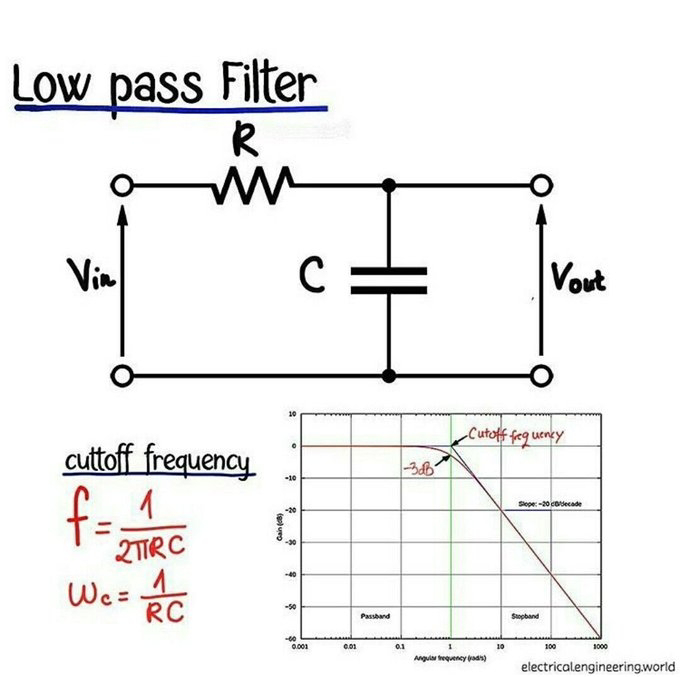
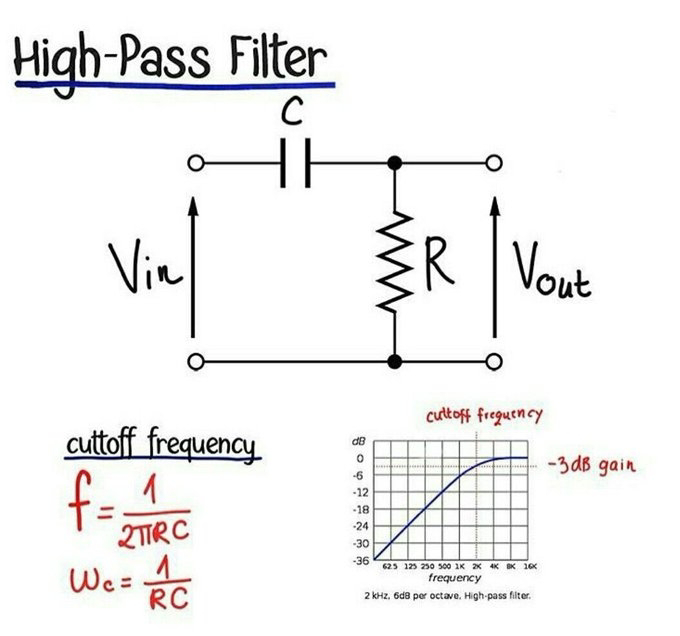
- Filters: To reduce noise in audio and electronic circuits.
- Timing Circuits: For controlling timing in various applications.
- Inverters and Power Supplies: To stabilize electrical power.
Conclusion
Capacitors are a crucial component in electronics, serving the purpose of energy storage and regulation. Their various types and characteristics make them suitable for a wide range of applications.